Current Issue
Energy Reduction in the Electronics Facility
Guidelines for creating and continuing a cost-effective program.
Electronics manufacturing facilities use a lot of energy to build product and support the infrastructure. There are potential areas and opportunities to reduce facility energy consumption. Furthermore, it can be demonstrated certain capital improvements have short returns on investment and meet the overall goal of reducing energy consumption and lowering operating costs.
Energy use. Most electronics manufacturing factories have many opportunities to reduce energy use. A few of the main areas to investigate and potentially reduce are lighting, manufacturing equipment, and facility equipment, including motors and humidification.
The following are guidelines for creating and continuing a facility energy reduction program:
- Use monthly or quarterly metrics to analyze the operation’s total energy use. Energy use is typically metered on a monthly basis. It is important to understand the total metered energy use in kilowatt per hour (kWh) and the total cost for the energy. Doing so will help quantify energy savings of improvements.
- Conduct an energy audit of the facility, focusing on facility equipment, lighting and manufacturing equipment. The goal of the energy audit should be to identify and prioritize process implementation opportunities or equipment improvements to decrease energy use.
- Identify rebates that may be available by the facility’s electric provider for equipment improvements. These rebates will help justify the ROI.
Potential energy reduction areas. Lighting is one of first areas to investigate and possibly improve. Lighting technology is ever-changing, with overall energy use decreasing per light fixture. The first step is to understand which lighting (bulb wattage and fixture) technology is in use at the facility. The next step is to understand the cost to upgrade the lighting to new technology such as LED. LED lighting uses less energy than traditional fluorescent bulbs, but the cost payback may or may not be acceptable depending on how much lighting the facility uses and what rebates are available from the electric provider.
Other potential lighting reduction areas:
- Install automatic light switches for conference rooms and offices and other rooms not in constant use.
- Implement a timer system for the production floor and office areas to turn the lights on and off in concert with work shift hours.
- Some lighting, such as fluorescent bulbs, can be upgraded with the existing light fixtures by changing the bulb only with energy-efficiency equivalents. Some lighting manufacturing companies may reduce the bulb wattage but keep the same lumen output.
Electronics manufacturing equipment uses a lot of energy. For these machines, the first step is to determine if the specific piece of equipment can be turned off to save on energy when not in use. Some equipment may not make sense to turn off. One example is a wave solder machine, as the solder pot takes several hours to reheat. Given the several hours it takes and manufacturing build requirements, this may not make sense to turn off to save on energy. This type of analysis is required to determine what makes the best sense for the operation.
Motors are used throughout every operation and are often overlooked. Motors are typically in a facility room to run compressors, pumps, water systems or many other purposes. Motors typically operate 24 hours a day to keep the manufacturing facility running. Older motors with higher horsepower (hp) have the potential to use the most energy. Similar to lighting technology, motor manufacturers continue to develop and release new products that use much less energy and are more efficient.
Electronics factories may use humidification equipment to increase the relative humidity for electrostatic discharge (ESD) products. Many different types of technology exist for creating humidification, such as electric, boiler stream, natural gas, compressed air and high pressure. Typically, electric humidification systems use the most energy. New electric systems may be more efficient, but the facility should investigate if a non-electric system, such as high pressure, compressed air, etc., will decrease energy consumption and achieve the operation’s humidification and manufacturing needs.
Energy evaluation and ROI examples. When conducting an energy evaluation to determine the ROI for equipment and capital energy improvements, the following data should be gathered:
- The total kilowatt per hour (kWh) of the current equipment and proposed new equipment.
- The availability of rebates from the electric company provider for the proposed energy savings.
- The ROI in years for the proposal. Depending on the operation, a return on investment of two years or less is generally deemed acceptable.
Electric motors are always a good starting point for energy improvements. A new high-efficiency motor may save enough energy to be justified, even with a 3% to 5% efficiency improvement, given many motors run 24 hours a day. The following example calculates the cost savings and time it will take to pay back the cost of upgrading an old 10 hp 85% efficiency motor with a new 95% high-efficiency equivalent.
FIGURE 1 details the energy used and saved by migrating to a new 95% efficient motor and running 24 hours a day for an entire year. The difference in kWh is 8,093 for one year. If the electric utility charge is 10 cents per kWh, the cost savings will be $809. If the new motor costs $800, the return on investment or simple payback will be approximately one year.
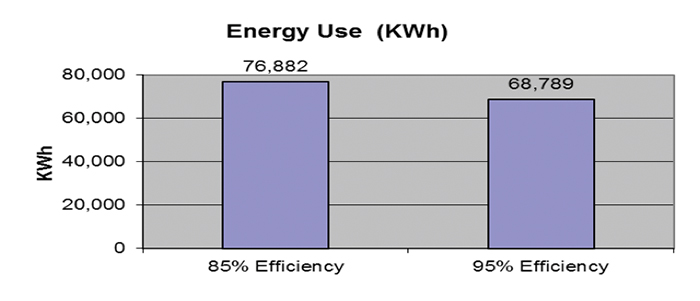
Figure 1. Energy use by efficiency.
The same methodology can be used for any energy improvement within a facility to understand the cost savings and ROI.
By understanding the energy consumption within a facility, the operation can investigate and justify energy cost savings. Many opportunities may exist to reduce energy, which will potentially help the company’s bottom line and save on energy, which also helps the environment.
is manufacturing staff engineer and environmental management representative, Benchmark Electronics (bench.com), and a contributing author to Green Electronics – Design and Manufacturing; scott.mazur@bench.com.
Press Releases
- Weller Tools Celebrates 80 Years of Innovation with Special Black Edition WE1010 and ZeroSmog Shield; Philippe Buidin Comments
- Saki America, Inc. Appoints Mario Ramírez Galindo as Project Engineer in Mexico; Craig Brown Comments
- BEST Inc to Host Soldering 101 Workshop at Illinois & Michigan Locations
- Incap Corporation: Incap's Annual and Sustainability Report 2024 published







